Product Type Carpet
Increase the comfort and warmth of your home with our beautiful and durable carpet options.

Carpet 101
Carpet adds comfort, insulation, and a cozy feel to any room. With endless colors, styles, and textures, it's easy to find your perfect match. Plus, many carpets are stain-resistant, odor-resistant, and trap allergens, making them low-maintenance and hypoallergenic. Use our guide to find the perfect carpet style, type and pattern for your home!
Glossary of Key Terms
Knowing carpet manufacturing terminology helps you understand the quality and true value when you are choosing a carpet for your home or office. Use our handy glossary to get you up-to-speed.
BACKING
Primary Backing – A woven or non-woven fabric into which the pile yarn is inserted by the tufting needles. Usually polypropylene.
Secondary Backing – Fabric laminated to the back of carpet to reinforce and increase dimensional stability. Usually woven polypropylene (ClassicBac®).
CUT PILE
A fabric whose face yarns are cut ends of pile yarn.
DENIER
Denier is a term used to describe the size of a yarn bundle. The higher the number, the thicker the yarn will be.
DENSITY
Determined by multiplying the face weight (oz/yd2) times 36 and dividing by the finished pile thickness. The factors that determine density are gauge, stitch rate, pile height, and yarn size.
GREIGE GOODS
Unfinished carpet as it comes off the tufting machine.
HEAT-SETTING
A process that locks the twist in the yarn. This is done by heating the yarn to a temperature that loosens the bonds between the molecules. New bonds are formed as the yarn cools (memory).
LATEX
A water emulsion usually consisting of styrene-butadiene synthetic rubber (SBR) compounded with large quantities of powdered fillers, usually calcium carbonate, used for locking yarn into primary backing and laminating secondary backing to tufted carpet.
LOOP PILE
Carpet style having a pile surface consisting of uncut loops.
PILE
The surface fibers or face yarn.
PILE HEIGHT
The height of the pile measured from the top of the primary backing to the top of the pile.
PLYING AND TWISTING
Two or more singles yarns are twisted together to form a plied yarn. Twist is measured as the number of turns per inch.
SHEARING
Carpet manufacturing process for producing a smooth carpet face on cut pile carpets.
SOLUTION DYED YARN
Fiber is colored by pigments mixed with the polymer chips prior to extrusion into fiber.
STITCH RATE
Number of yarn tufts per inch of lengths of a single tuft row.
WEIGHT
Face weight times the density.
Visual Characteristics, Fiber Types & Backing
The visual and physical texture of certain carpet styles are referred to as solids, tonals, and accents.
Visual Characteristics

Single colored effect with uniform texture.

Color is speckled, making it visually appealing and hiding stains and soil. Accents can be applied to both solids and tonals.

Tone-on-tone color variation that creates a textured aesthetic.
Fiber Types
Fiber Types
A process that locks the twist in the yarn. This is done by heating the yarn to a temperature that loosens the bonds between the molecules. New bonds are formed as the yarn cools (memory).
NYLON
Strengths: durable, resilient and dyeable.
Weaknesses: not inherently stain resistant. Shaw Floors nylon is treated with R2X® for stain resistance.
HIGH-PERFORMANCE P.E.T.
Strengths: durable, soft and fade resistant.
POLYESTER (P.E.T.)
Strengths: stain and fade resistant.
Weaknesses: not as resilient or durable as nylon.
POLYPROPYLENE (OLEFIN)
Strengths: inherently stain and fade resistant, lowest cost.
Weaknesses: lack of resiliency, limited styling, unstable raw material costs.
PROPRIETARY FIBERS
Most large manufacturers, such as Shaw and Mohawk, offer engineered fibers with additional performance characteristics.
Backings
Traditional carpet backing secures and holds the face fiber yarn in place. Backings may also feature protective treatments, including anti-stain or anti-static. Doing more than simply keep carpets in place, backings also:
- Improve insulation
- Reduce noise
- Increase softness and comfort
- Help resist wear and tear more effectively
- Provide improved tuft bind & lamination strength
- Prevent wrinkles and potential re-stretch issues
Most large manufacturers, such as Shaw and Mohawk, offer engineered backings with additional performance characteristics.
Construction–Pile
Carpet construction is a nuanced and intricate process that plays a pivotal role in determining the look, feel, and durability of the final product. Three primary carpet constructions dominate the market, each offering unique characteristics and aesthetic appeal: cut pile, loop pile, and cut and loop pile.
Cut Pile
Description—In cut pile construction, the carpet fibers are precisely cut at the top, creating a soft and even surface. This results in a plush texture that feels luxurious underfoot.
Characteristics—Cut pile carpets are known for their comfort, warmth, and a broad range of styles, from velvety Saxony to the more casual and textured frieze.
Loop Pile
Description—Loop pile carpets, as the name suggests, consist of uncut loops of yarn. The loops can be uniform or varied in height, creating diverse textures and patterns.
Characteristics—Loop pile carpets are renowned for their durability and resistance to crushing. They often present a more casual and contemporary aesthetic, making them suitable for high-traffic areas.

Cut and Loop Pile
Description—This construction combines both cut and looped fibers, offering a blend of textures. Patterns in carpets can be achieved through various techniques, including the arrangement of fibers, contrasting colors, and different pile heights.
Characteristics—Cut and loop pile carpets are visually interesting and sophisticated in appearance. They are versatile, allowing for the creation of intricate patterns, textures, and even sculptured effects. Patterned carpets can add visual interest and complement various interior styles. Popular patterns include geometric designs, florals, stripes, and intricate motifs.
Broadloom
Broadloom carpet, also referred to as tufted carpet, refers to wide rolls of carpet—typically 12’ or 15’ wide—that are installed over cushioned carpet padding and cut to size for wall-to-wall installation
Advantages
SEAMLESS APPEARANCE
Smooth and seamless, broadloom carpets create visually cohesive flooring surface.
COMFORT
Generally softer underfoot, due to padding. Ideal for rooms where comfort is a priority.
INSULATION
Offers better insulation against sound and temperature, creating quieter and warmer environments.
VARIETY
Allows for a wide range of design options with many patterns and customizability.
EASY INSTALLATION
Faster and more efficient installation over large areas compared to individually placing carpet tiles.
Considerations
MAINTENANCE
Stains and damage can be challenging to address. Replacing a damaged section may require replacing the entire carpet, affecting cost and convenience.
WASTE
Specific widths can lead to more material waste during install, especially when cutting and fitting to room dimensions.
LIMITED DESIGN FLEXIBILITY
Less flexible in terms of design changes as the entire carpet must be replaced for a new look.
COST
Can be more expensive upfront, from both material and installation costs.
Construction
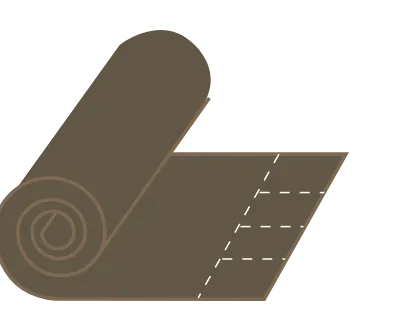
Comes in rolls up to 100 feet—available for purchase by the linear foot. To calculate square yards: divide the length in feet by 3, then multiply by 4 to get square yards.
Tiles and Planks
Carpet tiles, also known as carpet planks, modular carpets and carpet squares are manufactured in pre-sized shapes with integrated backing. They are primarily used for office environments but recently have become popular for residential installations too.
Advantages
EASY INSTALLATION
Less complicated than traditional broadloom installs, carpet tiles and planks are great for DIY projects.
CUSTOMIZATION
Mix and match colors, patterns, and textures to create flooring designed to your specific taste and style.
MODULA
Easily replace individual stained or damaged squares instead of the entire carpet.
DURABILITY
Can withstand heavy foot traffic better than traditional carpeting and are easier to replace.
COST-EFFECTIVE
Ease of installation and durability mean lower labor costs and lower long-term maintenance expenses.
Considerations
Appearance Limitations
Seams between tiles may be visible, resulting in a less cohesive look.
INITIAL COSTS
High-quality carpet tiles and adhesive materials may have a higher initial cost than budget-friendly traditional carpets.
MOISTURE ISSUES
If liquids penetrate the seams, it can lead to mold or mildew growth in some carpet tiles making them less suitable for areas prone to frequent spills or high humidity.
SUBFLOOR PREPARATION
For optimal installation, the subfloor must be smooth and well-prepared. Uneven subfloors can lead to undesired finished results.
LIMITED CUSHIONING
Tiles may not provide the same level of cushioning, making them less suitable in areas where comfort is a priority.
Shapes and Patterns

Next Steps
Learn what to expect before, during and after your professional flooring is installed and what steps to take to keep your
flooring looking brand new for years to come. All this and more from your experts at Thornton Flooring.
Design Consultations
Call today to schedule a time for one of our flooring experts to visit your home and provide professional measurements & estimates for your next project, entirely free of charge. There’s no obligation to purchase from us after your appointment. We’re simply here to make sure you get the right solution for your needs at the right price.




